
Optionally, IPSecurity can be configured to provide data encryption and confidentiality. Once setup, DMVPN continues working around the clock, creating dynamic VPNs as needed and keeping every router updated on the VPN topology. DMVPN simplifies greatly the WAN network topology, allowing the Administrator to deal with other more time-consuming problems. Spoke routers are able to dynamically create VPN Tunnels between them as network data needs to travel from one branch to another. Dynamic Creation of Spoke -to-Spoke VPN Tunnels.Thanks to NHRP, Spoke routers rely on the Hub router to find the public IP Address of other Spoke routers and construct a VPN Tunnel with them. Spoke routers can use dynamic public IP Addresses.
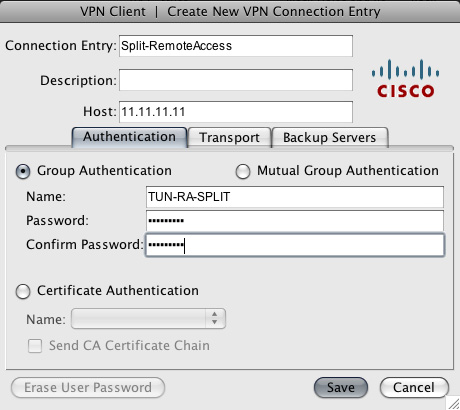
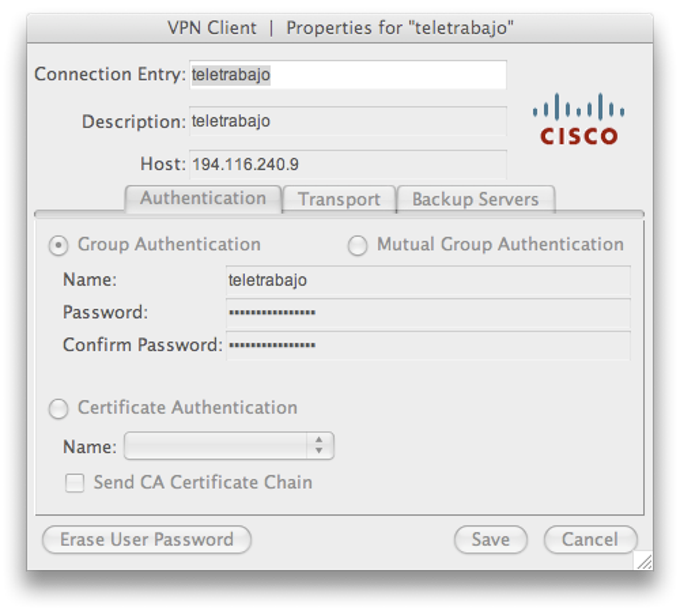
CONFIGURING CISCO VPN CLIENT FULL
Full Support for Spoke Routers with Dynamic IP Addressing.No matter how many Spoke routers connect to the Hub, the Hub configuration remains constant. A single mGRE, IPSec profile without any crypto access lists, is all that is required to handle all Spoke routers. No more multiple tunnel interfaces for each branch (spoke) VPN.
DMVPN BenefitsĭMVPN provides a number of benefits which have helped make them very popular and highly recommended. NHRP fills this gap by telling mGRE where to send the packets. Because mGRE tunnels do not have a tunnel destination defined, they cannot be used alone. It is important to note that mGRE interfaces do not have a tunnel destination. MGRE Tunnel Interface is used to allow a single GRE interface to support multiple IPSec tunnels and helps dramatically to simplify the complexity and size of the configuration.įollowing is an outline of the main differences between GRE and mGRE interfaces: The Hub maintains a special NHRP database with the public IP Addresses of all configured spokes.Įach spoke registers its public IP address with the hub and queries the NHRP database for the public IP address of the destination spoke it needs to build a VPN tunnel. The Hub router undertakes the role of the server while the spoke routers act as the clients. NHRP is layer 2 resolution protocol and cache, much like Address Resolution Protocol (ARP) or Reverse ARP (Frame Relay). In both cases, the Hub router is assigned a static public IP Address while the branch routers (spokes) can be assigned static or dynamic public IP addresses.ĭMVPN combines multiple GRE (mGRE) Tunnels, IPSec encryption and NHRP (Next Hop Resolution Protocol) to perform its job and save the administrator the need to define multiple static crypto maps and dynamic discovery of tunnel endpoints.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
